Learn about the human digestive system’s structure and function, from mouth to rectum, and understand the processes involved. Human Digestive System.
ALIMENTARY CANAL (HUMAN DIGESTIVE SYSTEM)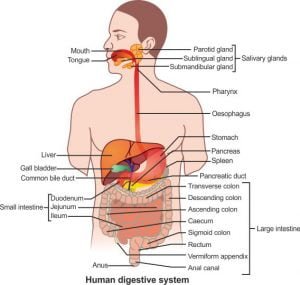
Long, coiled tube of varying diameter extending from mouth to anus (8-9m in length)
Consists of : a) Mouth and Oral cavity, b)Pharynx, c)Esophagus, d)Stomach, e)Intestine
Mouth and Oral cavity
- Mouth is a small transverse aperture bordered by two fleshy moveable lips
- Oral cavity (Buccal cavity) is spacious chamber including palate, tongue and teeth
- Roof of oral cavity is formed by hard palate, Base by soft palate and floor by tongue and sides by cheeks.
Pharynx
- It is wide opening at back of mouth cavity.
- It leads to two openings: gullet (leads to esophagus) and glottis (leads to larynx).
- There is a muscular flap called epiglottis which closes glottis when food is swallowed.
- There are 2 openings of internal nares above and two openings of Eustachian tubes at the sides. It is the only part common to digestive and respiratory system.
Oesophagus
- It is a long (about 25 cm) narrow muscular tube which connect mouth to stomach.
- It runs behind the trachea pierces diaphragm to open into stomach.
- It undergoes peristalsis to carry down food and water or fluid from pharynx to stomach.
Stomach
It is a large muscular part of Human Digestive system, J shaped elastic bag situated below diaphragm on left side of abdominal cavity . It has four parts
1.Cardiac: it is so called because it lies near heart. In between oesophagus and cardiac part of stomach there is cardiac sphincter.
2.Fundus: it extends superiorly from the cardiac part. It is usually filled with air.
3.Body: it is main part of stomach.
4.Pyloric part: it is distal part of stomach. it opens into duodenum. It opens and closes several times. At the time of opening, a small amount of partially digested food(chime) is passed into duodenum.
- Gastric gland secretes gastric juice.
Intestine
Long coiled tube of about 8m long divided into small intestine and large intestine
Small Intestine (6m long)
It is divisible into 3 parts.
1.Duodenum: It is c shaped and about 25 cm long. It receives bile juice and pancreatic juice through common bile duct.
2.Jejunum: It is about 2.5 meter in length. It is coiled part.
3.Ileum: It is about 3.5 meter long. It is highly coiled part. Both jejunum and ileum are suspended by mesenteries. The inner wall of ileum has number of folds called villi. It is mainly for digestion and absorption.
Large intestine
It is about 1.5 meter long and divisible into following parts;
1. Caecum: It is pouch like structure about 6 cm long. There is ileocaecal valve preventing back flow. Attached to caecum is a slender vermiform appendix of about 10 cm long. It is vestigial in man but functional in herbivores. The inflammation of appendix is called appendicitis at the time of infection.
2.Colon: It is inverted U shaped and divisible into
Ascending colon: It is the first part on right side. It moves upward from caecum.
Transverse colon: It is horizontal part.
Descending colon: It moves down at left side. It descends down
Pelvic colon: It is s shaped or sigmoid. Undigested material can remain in colon for about 36 hours.
- Colon is for absorption of water mainly.
Rectum:
Small muscular region, straight, about 15 cm long. It opens to the exterior through anus. Undigested material remains here for a short time. The anus is guarded by 2 sphincters Throughout the alimentary canal, mucous glands secrete mucus.

