What is sulfur?
Sulfur is a chemical element with the atomic number 16 and the symbol S. It is a nonmetallic element that is among the most prevalent in the universe. Sulfur is well-known for its characteristic yellow color and pungent stench. It is frequently employed in a wide range of industrial applications, including the manufacture of fertilizers, medicines, and rubber goods. In addition to its commercial use, sulfur is a key component of many amino acids and proteins and plays a significant part in biological processes. The deatil on sulfur cycle will be studied in this article.
Steps of Sulfur cycle
The sulfur cycle is a biogeochemical cycle in which sulfur moves through the biosphere, hydrosphere, atmosphere, and lithosphere. It is comprised of the following steps:
- Sulfur enters the atmosphere naturally through volcanic eruptions as well as the weathering of rocks.
- Sulfur dioxide gas is subsequently transformed into particles of sulfate by oxidation, an action facilitated by bacteria and other microbes.
- Plants may absorb sulfate particles and utilize them to produce organic compounds such as amino acids & proteins.
- Animals and humans get sulfur from plants or other species that have absorbed sulfur.
- When organisms such as animals and plants die, the sulfur in their dead bodies gets released to the soil. It occurs via decomposing and mineralization processes, where it may be absorbed by new plants.
- Anaerobic bacteria can convert part of the sulfur in the soil into hydrogen sulfide gas. It can be discharged into the atmosphere or utilized by other bacteria to generate sulfuric acid.
- Human activities such as the combustion of fossil fuels and industrial operations can also emit sulfur to the earth’s atmosphere.
- Once in the atmosphere, sulfur may combine with other compounds to generate acid rain. It can be detrimental to the environment and human health.
- Rainwater may also deposit sulfur into bodies of water, where it can be consumed by aquatic creatures or transformed into hydrogen sulfide gas by anaerobic bacteria.
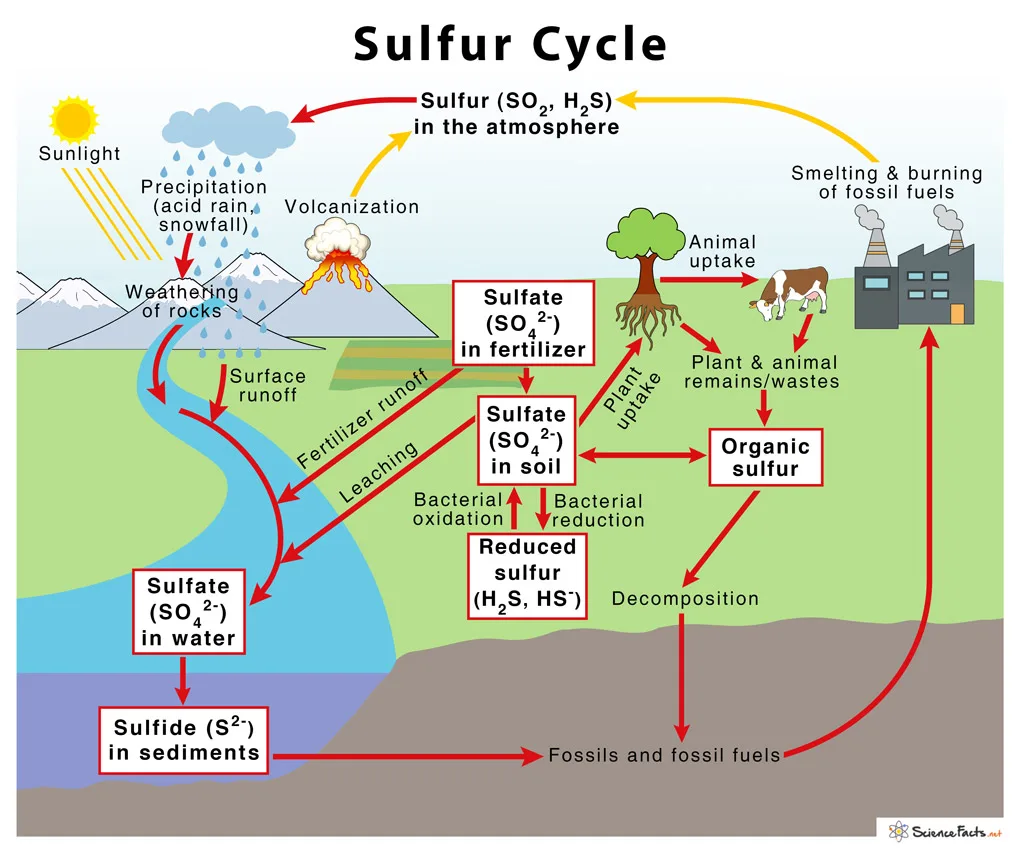
Understanding the sulfur cycle is critical for regulating the environmental implications of human activities and preserving ecosystem sustainability.
Importance of sulfur cycle
The sulfur cycle is a critical biogeochemical cycle that is important for the proper functioning of ecosystems and the overall health of our planet. It is essential for the following reasons:
- Nutrient cycling: Sulfur is an essential nutrient for living organisms, as it is required for the formation of amino acids and proteins. The sulfur cycle assures that sulfur is accessible for usage in plant and animal development and metabolism.
- Acid rain: The sulfur cycle has been implicated in acid rain formation. When sulfur dioxide gets released into the atmosphere, it can react with chemical compounds to generate acid rain, which is damaging to both the environment and the health of humans. Understanding the sulfur cycle is critical for regulating the effects of acid rain and mitigating its detrimental consequences.
- Geological processes: Sulfur is involved in geological events such as rock weathering and mineral formation. The cycling of sulfur aids in the regulation of these activities and in the preservation of a stable sulfur equilibrium in the environment.
- Carbon cycling: The sulfur cycle is inseparably connected to the carbon cycle, as sulfur compounds in the atmosphere may influence cloud formation and sunlight reflection, hence influencing world temperatures and climate patterns.
- Human activities: Human activities such as the combustion of fossil fuels and industrial operations. It can emit sulfur dioxide and other sulfur compounds into the atmosphere, which can harm the quality of water and air. Studying the cycle is critical for mitigating the effects of these activities and supporting environmentally friendly behaviors.
Lear more:
Human impact on sulfur cycle
Human activities have a considerable impact on the sulfur cycle, which has both beneficial and bad environmental consequences. Effects of human activities on the sulfur cycle are as follows:
- Fossil fuel combustion: The burning of fossil fuels emits huge volumes of sulfur dioxide into the atmosphere. This can result in the generation of acid rain, which is harmful to the environment and human health.
- Industrial operations: Sulfur dioxide and other sulfur compounds are released into the atmosphere by many industrial activities, including metal smelting and paper manufacture. This can contribute to acid rain and other harmful environmental impacts.
- Agriculture: The use of sulfur-containing fertilizers can raise sulfur levels in the soil and groundwater. This has the potential to harm aquatic ecosystems and water quality.
- Mining: Mining activities can cause sulfur-containing minerals to be released into the environment, contributing to acid mine drainage and other detrimental effects on water quality.
- Garbage disposal: Improper disposal of sulfur-containing garbage, such as batteries and electronic equipment, can result in sulfur emission into the environment.
Overall, human activities can disrupt the natural balance of the sulfur cycle, leading to negative impacts on the environment and human health.