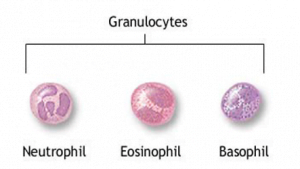
- PMNs are composed of three cell types; neutrophils, eosinophils and basophils, based on their staining characteristics with certain dyes.
- Also called granulocytes since they consist of many granules consisting lytic enzymes.
- These cells are predominantly important in the removal of bacteria and parasites from the body.
- They engulf these foreign bodies and degrade them using their powerful enzymes.
- NEUTROPHIL
- Multi-lobed nucleus, 11-14 μm
- 50-70% of circulating WBC (higher numbers suggestive of bacterial infection)
- 7-10 hours in circulation and then migrate to tissue, life 3-4 days
- The fine granules stain poorly with acidic and basic dyes neutrophil.
- Phagocytosis and killing of ingested microorganisms.
- Granules contain bactericidal enzymes; eg. Lysozyme, myeloperoxidase; neutral proteases (i.e. elastase); acid hydrolases (B-glucoronidase), collagenase and lactoferrin and cathepsin B.
- The phagosome fuses with granules to destroy internalized bacteria by oxygen dependent respiratory burst.
- Neutrophils are the 1st cells to arrive. A number of substances produced during an inflammatory response recruit neutrophils to a site of inflammation.
- EOSINOPHIL
- Represent 1-3% of circulating WBCs, 11-15 μm
- Possess a bi-lobed nucleus and a heavily granulated cytoplasm.
- Granules stain orange/red with the acidic dye Eosin Y.
- Somewhat phagocytic but DO NOT act as APCs.
- The major role of the eosinophil is believed to be against parasites, particularly parasitic worms.
- Eosinophils kill by ADCC [antibody dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity] by binding to parasite – specific IgE via cell surface
- When eosinophils bind to IgE on the surface of a worm, the cell is triggered to degranulate. The contents of the granules cause
damage to the worm’s tegument. - One component unique to the eosinophils – and highly toxic to worms – Major Basic Protein (MBP).
- BASOPHIL
- Only present in the bloodstream, and represent 0.2 % of circulating WBC
- Lobed nucleus – more variable, large coarse granules stain blue with basic dye methylene blue.
- They play a major role in the allergic response when they release their granules (containing histamine, serotonin, heparin, prostaglandin, etc into the bloodstream following exposure to specific allergens).
- Basophils bear Fc receptors for IgE (FceRs)
- When an individual is exposed to an allergen, allergen specific IgE is produced. This IgE binds to the surface of basophils [in the sensitization phase of the allergic response].
- Upon re-exposure to the allergen, the allergen binds to IgE on the surface of basophils resulting in degranulation [effector phase].