What is carbohydrate?
Biomolecules are large macromolecules that include carbohydrates, proteins, lipids and nucleic acids that help in functioning and development of living cells. Among these four, carbohydrate is the basic food group that is a key source of energy and helps us in maintaining healthy diet.
Carbohydrate consists of carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O) atoms where aldehydes and ketones are two basic compounds that build up the carbohydrate. Aldehyde is a compound made up of carbon and oxygen atoms which are joined with double bond and together a single bond with hydrogen atom and another functional group of atom. Ketone is a compound made up of double bonded carbon and oxygen atom with two carbon atom additionally.
Carbohydrates are found in every food like grains, cereals, vegetables, fruits, milk products. Bread, potatoes, rice, beans are carbohydrate rich foods that one gram of carbohydrate contains about 4 kilocalories (Kcal) of energy which is as same amount of protein.
Functions of carbohydrate:
- Carbohydrate acts as a fuel for our body with energy including working muscles, develops proper functioning of brain and central nervous system.
- It provides structural framework for building RNA and DNA.
- It is also essential for the oxidation of fats and acts as precursors for many organic compounds.
- It also provides cellular structure like cell membrane, cell wall and for cellular functions as glycoprotein and glycolipid.
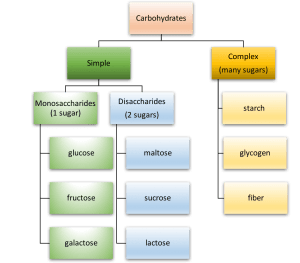
Classification of carbohydrates
(Source: https://media.lanecc.edu/users/powellt/FN225OER/Carbohydrates/FN225Carbohydrates2.html )
Carbohydrates are of two main types:
- Simple carbohydrate
- Complex carbohydrate
Simple carbohydrate
- Simple carbs contain one or two sugar units therefore; they are absorbed and digested quickly by our body.
- The single sugar unit is called monosaccharide that is glucose that plants produce during photosynthesis. Glucose is available in fruits, vegetables, corn syrup and high fructose corn syrup, in milk and milk products as galactose and in fruits and vegetables as fructose.
- Disaccharides are made up of two sugar units which are of three types. If two glucose sugars bind together, it forms maltose. Maltose is found in malted wheat and barley, sweet potatoes, breads and molasses. They are also found in sprouted grains.
- Sucrose is a combination of glucose and fructose molecules which is naturally available in fruits and vegetables. Plant containing sucrose such as sugar cane and sugar beets are used to make refined table sugar. Sucrose can be found in maple syrup and honey which is a fuel for our brain and nervous system.
- When glucose molecules bind with galactose, then lactose is formed which can only be found in milk and milk products like cheese and yoghurt. It is the only animal based carbohydrate as most of the carbohydrates are obtained from plant foods.
Complex carbohydrate
Complex carbohydrate contains more than two sugar units and is called polysaccharides. They are digested at lower rate than simple sugars. Simple carbs relatively increases blood sugar level but complex carbs provide long term energy.
There are three main types of polysaccharides:
Starch
- Starch is found in plants in storage form like seeds, grains, legumes, nuts, potatoes, turnips and carrots.
- If starch are formed in straight chain, then they are called amylase and amylopectin if they are in branched chain.
Glycogen
- Glycogen is found in animals in storage form in liver and skeletal muscles. Its structure is similar to amylopectin.
- Liver glycogen breaks down into simple glucose and uses by the cells whereas muscle glycogen breaks down to provide energy.
Fiber
- Fiber can be found in whole plant foods like whole grains, nuts, fruits, vegetables. Cellulose is one of the most common plant fibers.
- Fibers are not broken down and digested by our human body because we lack fiber digesting enzyme, instead it passes undigested.
- It helps in maintaining blood sugar level and keeps hunger in check.
Learn More
Health benefits of carbohydrates:
Energy source
- Carbohydrate is a major source of energy to our body and brain to function and metabolize properly.
- Carbohydrate when consumed gets broken down into a simple sugar and our bloodstream absorbs them and provides us energy.
- If we don’t take enough carbohydrate, our glucose level decreases that lead us to weakness, experience brain fog and memory loss.
Heart health
Eating whole grain foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole wheat grains provide enough fiber that helps in protecting heart from blockage and heart attack. These foods are low in fat and reduce cholesterol.
Reduces bloating
Complex carb leads to excess gas and bloating in the stomach therefore, simple carb should be taken that helps in maintaining and improving digestive system and reduces bloating.
Prevents weight gain
High fiber diet is effective in weight loss than the carbohydrate that contains low fiber. Fibers are digested slowly by our body hence keeping us full for a longer time.
Prevents cancer risk
Good carbs such as whole grains, fruits, vegetables, beans contain anti-oxidants and anti-cancer effect which helps in reducing the risk of lung and bowel cancer.
Improves muscle mass
Intake of proper amount of carb helps in high intensity workout as the body converts glycogen into energy forming ATP molecules required for the workout for an hour.
Health risk of carbohydrates
Weight gain
People who consumed refined foods are likely to gain weight than who consumed whole grain foods.
Refined food products such as chips, soda, cookies, cakes increases blood sugar level and body weight significantly.
Obesity and stroke
Refined carbohydrate food products leads to an abdominal obesity which is associated with increase cholesterol level, heart disease and strokes
Insulin resistance
Insulin level becomes resistant which eventually results in Type 1 and 2 diabetes and also increases blood pressure.
Increased Triglycerides
Triglyceride is a type of fat found in our bloodstream, which when increases, clogs the arteries and causes heart attack.
Therefore, the daily recommended sugar intake by Mayoclinic.com is maximum 6-9 teaspoons.
Carbotoxicity
Excessive intake of refined and processed carbohydrate to digestible polysaccharides that causes toxicity on human health is referred as carbotoxicity.
It is a chronic disease in molecular and cellular level that occurs in accelerated aging.
Many articles have outlined the dietary plans to avoid carbotoxicity.
References:
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/161547#high-carb-or-low-carb-diet
- https://www.livescience.com/51976-carbohydrates.html#:~:text=Carbohydrates%20are%20the%20sugars%2C%20starches,important%20to%20a%20healthy%20diet.
- https://www.diabetes.org/nutrition/understanding-carbs/types-carbohydrates
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/15416-carbohydrates
- https://media.lanecc.edu/users/powellt/FN225OER/Carbohydrates/FN225Carbohydrates2.html
- https://www.conserve-energy-future.com/benefits-eating-carbs.php
- https://healthyeating.sfgate.com/major-side-effects-carbohydrates-human-body-10627.html