Introduction
Contraception is defined as an intentional prevention of conception through the use of various contraceptive measures / methods. According to World Health Organization, among the total women of reproductive age group, 842 million are using contraceptive methods and 270 million have an unmet for contraception.
What are the criteria of ideal contraception?
- It should be widely acceptable
- Inexpensive
- Simple to use
- Safe
- Highly effective
- Requiring minimal motivation, maintenance and supervision
What are the factors affecting choice of contraception?
- Availability and cost
- Age and parity of couple
- Reliability
- Side effects and contraindications to a particular method
- Advantages and disadvantages
- Requirement of follow-up
Methods of contraception/ Contraceptive measures
| Temporary | Permanent |
| Barrier method | Female: Tubectomy |
| Natural contraception | Male: Vasectomy |
| Oral contraceptive pills | |
| Injectables | |
| Implants | |
| Intrauterine contraceptive devices |
Barrier method
| Males | Females |
| Condoms | Female condoms (Fem shield) |
| Today contraception/vaginal sponge | |
| Vaginal diaphragm/cervical cap |
Condoms as Contraceptive measures

Types of Condoms:
- Latex
- Polyurethane
- Vylex
- Poly isoprene
- Natural membrane condoms
Effectiveness of Condom
- 2 pregnancies per 100 women per year with consistent and correct use
- 13 pregnancies per 100 women per year as commonly used
Advantages of Condom
- Very good protection against sexually transmitted diseases.
- Reduces the chances of developing cervical cancer by preventing HPV infection.
- Can be used after vaginoplasty
- Can be used as tamponade for managing atonic post partum hemorrhage
Disadvantages of Condom
- There is a chance of accidental breakage or slippage of condom during
- Inadequate sexual pleasure
- Allergic reaction to Latex
Female condom as Contraceptive measures
It is a pouch made of polyurethane. It lines the vagina and also the external genitalia. At each end, there is one flexible polyurethane ring. Length of female condom is about 17 cm.

Effectiveness of Female Condoms
- 5 pregnancies per 100 women per year with consistent and correct use
- 21 pregnancies per 100 women per year as commonly used
Advantages of Female Condom
- It prevents from sexually transmitted diseases
Disadvantages of Female Condom
- Increased risk of UTIs
- Interferes with sexual pleasure
- If there is case of uterine prolapse, cystocele, rectocele or retroverted uterus, it is unsuitable.
Vaginal sponge as Contraceptive measures
It is a mushroom shaped polyurethane disposable sponge. It contains 1 gm of nonoxynol-9 and is provided with a loop for easy removal. It should be placed high up in the vagina with concave side covering the cervix and should be kept for 6 hours in the vagina after intercourse. It prevents entry of sperm into the cervical canal and contains spermicidal agents.

Disadvantages of Vaginal sponge
- Allergic reaction
- Vaginal dryness, soreness, or itching
Vaginal diaphragm | Cervical caps as Contraceptive measures
It is an intra vaginal device made up of latex. It has flexible metal or spring at the margin. It requires medical or paramedical personnel to measure the size of the device. It requires additional chemical spermicidal agent on the superior surface of the device during insertion. The device should be introduced 3 hours before intercourse and is kept for atleast 6 hours after the last coital act.
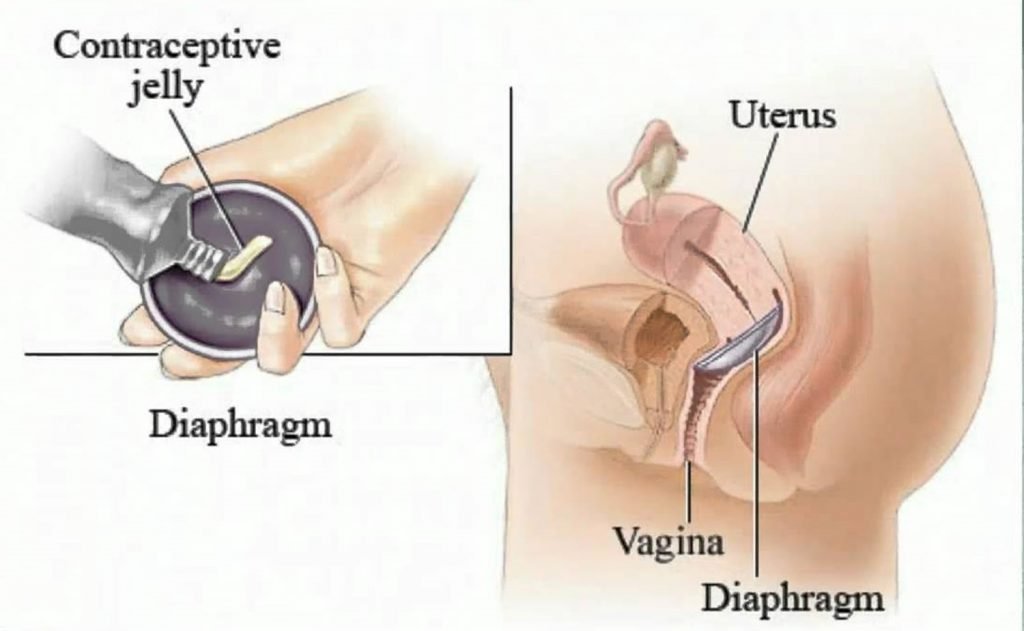
Advantages of Vaginal Diaphragm
- Prevents the spread of sexually transmitted diseases.
Disadvantages of Vaginal Diaphragm
- They do not protect against HIV
- Increases the chance of UTI and cervical erosion
Contraindication of Vaginal Diaphragm
- Prolapse, cystocele, rectocele
- Retroversion of uterus
- Genitourinary fistula
- Lacerated cervix
- Recurrent UTI
Natural contraception Methods
- Calendar method
- Basal body temperature method
- Cervical mucus method
- Sympatothermal method
- Lactational amenorrhea method
- Coitus interruptus
Calendar/Rhythm Method
It is based on the theory that ovulation occurs on day 14 +/- 2 days in a female with 28 days cycle and life span of fertilizable sperm is 48-72 hours and ova is 12-24 hours. Thus, unsafe period is the between 8-18 day.

Effectiveness of Rhythm Method
- 15 pregnancies per 100 women per year as commonly used
Advantages of Rhythm Method
- Low cost and lack of side effects
Disadvantages of Rhythm Method
- In case of irregular cycle it is difficult to predict safe period
- In postnatal period, it is not applicable
- It requires high degree of motivation
Basal body temperature method
It is based on the theory that, during ovulation there is rise in body temperature by 0.2-0.5 degree Celsius that persists for at least 3 days. Thus the safe period is from 4th day, first day being the day of ovulation to the last of next period. It is very difficult to accurately know the safe period by this method
Cervical mucus method
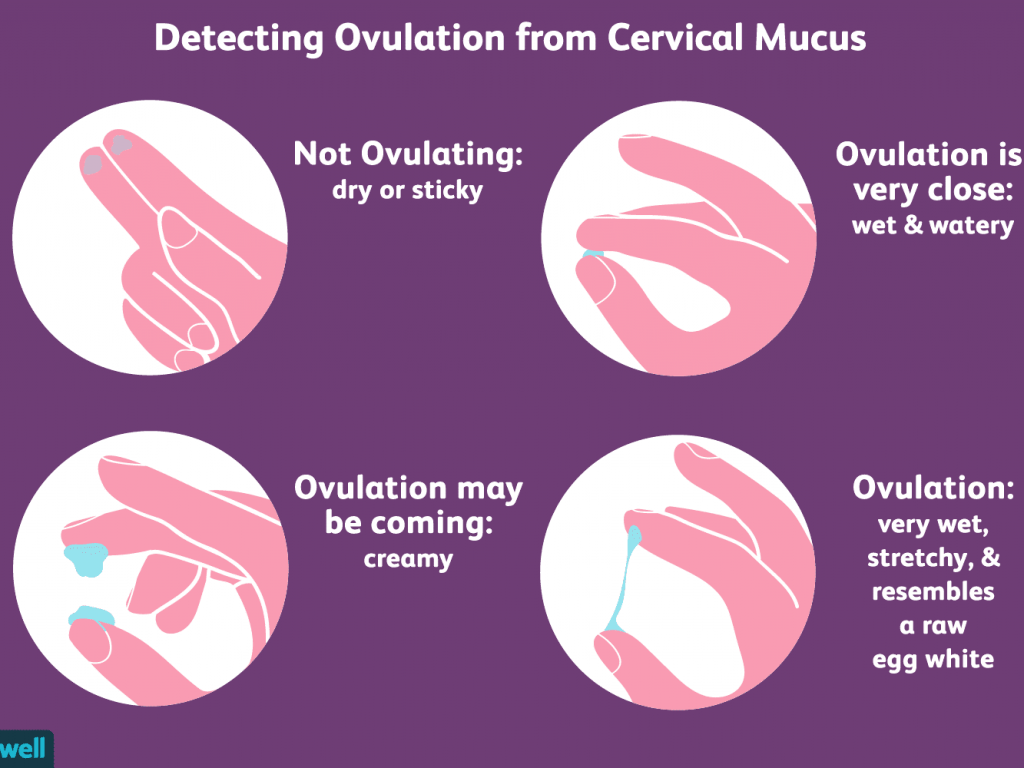
It is based on the principle that, at the time of ovulation, cervical mucus is watery, clear, smooth, slippery and profuse and after ovulation, the mucus becomes thick, scanty and loses its elastic nature. Thus, intercourse is safe during dry days immediately after the menses and till mucus is detected.
Sympatothermal method
This method uses the 2 indicators (cervical mucus method and basal body temperature) to identify the fertile period.
Effectiveness of Sympatothermal method
- Less than 1 pregnancies per 100 women per year with consistent and correct use
- 2 pregnancies per 100 women per year as commonly used
Lactational amenorrhea method
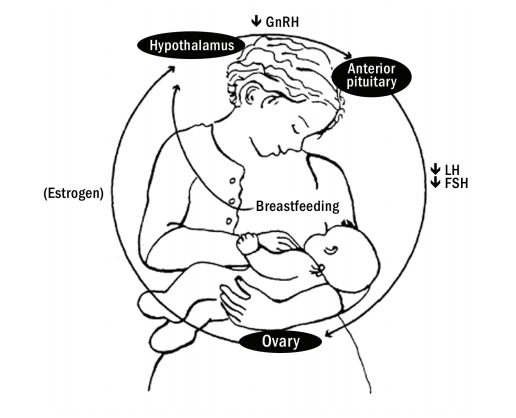
It is based on the principle that, during lactation due to release of prolactin ultimately leads to an anovulation and amenorrhea. Those who are exclusively breast feeding, contraceptive benefits are for 3rd postpartum month and those who are partially breast feeding, it is for only 3rd postpartum week.
Effectiveness of Lactational amenorrhea method
- 0.9 pregnancies per 100 women in six month with consistent and correct use
- 2 pregnancies per 100 women in 6 month as commonly used
Coitus interruptus/ Withdrawal methods
In this method male partner withdraw the penis shortly before ejaculation. It is most widely used contraceptive method by man.
Effectiveness of Coitus interruptus/ Withdrawal methods
- 4 pregnancies per 100 women per year with consistent and correct use
- 20 pregnancies per 100 women per year as commonly used
Learn more:
References
- Shaw’s Textbook of Gynecology; 16TH Edition
- DC DUTTA’s TEXTBOOK OF GYNECOLOGY; 6th Edition
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3307935/
- https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/family-planning-contraception
- http://resources.jhpiego.org/system/files/resources/lam_mnch_manual_0.pdf