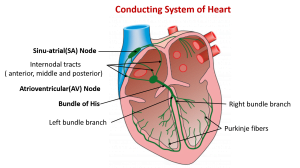
Heart has intrinsic system whereby muscle contracts and relax without the involvement of brain. However, Intrinsic system can be stimulated or depressed by nerve impulses initiated by brain or hormones. The origin, conduction and regulation of heartbeat involves Sino-Atrial node (SA Node), inter-nodal pathways, atrioventricular node (AV Node), the AV bundle and the bundle of Purkinje fibers .
SA node
- SA node is a small, flattened mass of neuromuscular tissue, about 3mm wide, 15mm long and 1mm thick.
- It is situated near the opening of superior venacava in right atrium.
- Sinus nodal fibers connects directly with the atrial muscle fibers so that any action potential that begins in the sinus node transmits immediately into atrial muscle wall.
Fibers of SA node
- The fibers of SA node has ability of self excitation and control the rate of entire heartbeat.
- The fibers of SA node have high concentration of Sodium ions in extracellular fluid and negative charges inside the nodal fibers. Due to high concentration and the presence of open channels, Na+ ions always tends to enter inside.
- The membrane permeability of K+ is gradually reduced which upsets the ionic balance of Na and K making the interior more positive.
- Ultimately at threshold (approx. -40mV), fast Ca++ channels open allowing entry of Calcium and some Sodium form extracellular space.
- The increase in Ca++ produces rising phase of action potential and reverses the membrane potential. In this way excitation wave or electrical waves are generated.
- At regular intervals, the wave of contraction spreads all over the atria. The SA node sets the pace for the heart as a whole. Hence it is the heart’s pacemaker.
- The fibers of SA node are closely associated with atrial muscle hence action potential generated at SA node travels throughout the atria.
- This ultimately stimulates AV node through internodal pathway which is present in the posterior wall of septum of right atrium.
Atrioventricular node (AV node)
- Atrioventricular node (AV node) is a small mass of neuromuscular tissue located in the wall of atrial septum near atrio-ventricular valves.
- At AV node impulse is delayed for about 0.1 sec allowing the atria to complete their contraction before the ventricles contract.
- The AV node is also capable of initiating impulses of contraction but at slower rate than SA node.
Atrioventricular bundle / AV bundle / Bundle of His
- Atrioventricular bundle / AV bundle / Bundle of His is a mass of specialized fibers originating from AV node.
- AV bundle crosses the fibrous ring that separate atria and ventricle. And divides into right and left branches at upper end of septum.
- Within the ventricular myocardium these branches breaks down into fine purkinje fibers.
- Purkinje fibers convey impulses of contraction from AV node to the apex of myocardium where the wave of ventricular contraction begins and sweeps upwards, pumping blood into pulmonary artery and aorta.
Regulation of Heartbeat
Heartbeat is regulated by both hormonal and nervous control
Nervous control
Heart is abundantly supplied with parasympathetic (vagus) and sympathetic nerve fibers. Impulse originated in heart is increased by Sympathetic nervous system (SNS) and decreased by parasympathetic nervous system (PNS). Stimulation of right vagus slows the heart by inhibiting SA node whereas stimulation of left vagus slows AV conduction.
Hormonal control
The hormones adrenaline and non-adrenaline control heart activity.