Vitamins are a group of organic molecules that is essential micronutrients required for metabolism and nutrition. Vitamins are not synthesized by our body therefore it must be obtained through a diet even in small quantities. Discover the sources and functions of vitamins. Learn about their Vitamins sources and functions, classification and daily intake recommendations for optimal health.
- The name “vitamin” was taken from the word “vitamine” by Polish biochemist Casimir Funk in 1912. Food was the only source of vitamins back then which resulted in vitamin deficiency disease in many people who were not able to afford nutritional foods. Then, vitamin tablets and supplements were commercially produced and made available that prevented vitamin deficiency among the general population. The government also recommended and mandated the addition of vitamins in food such as flour and milk which is termed as food fortification.
- In humans there are 13 essential vitamins required for our body in a small amount to function properly:
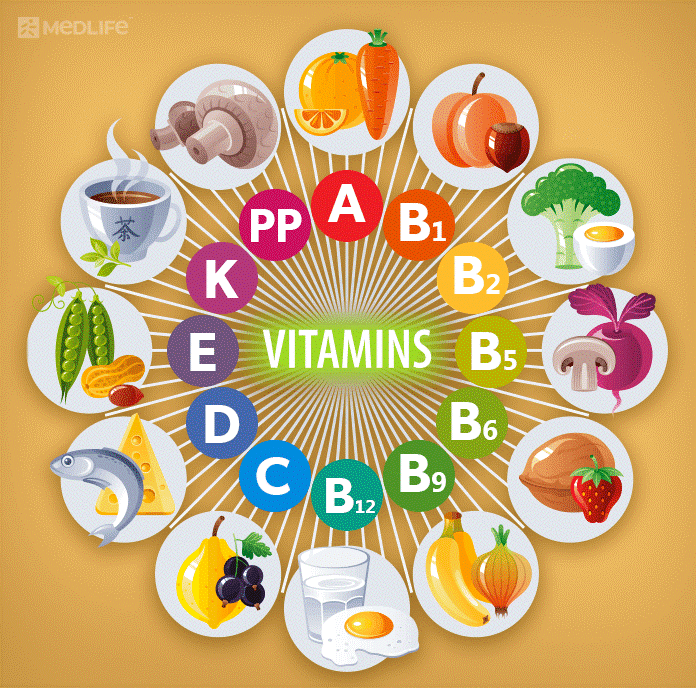
(Source:https://www.medlife.com/blog/vitamins-benefits-deficiency-test-diet/)
- Vitamin A (retinoic acid)
- Vitamin C (ascorbic acid)
- Vitamin D (calciferol)
- Vitamin E (alpha-tocopherol)
- Vitamin K (phylloquinone, menadione)
- Vitamin B1 (thiamine)
- Vitamin B2 (riboflavin)
- Vitamin B3 (niacin)
- Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic acid)
- Vitamin B7 (Biotin)
- Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine)
- Vitamin B12 (cobalamin)
- Vitamin B9 (Folic acid)
Vitamins are classified into two groups:
- Fat-soluble vitamins
- Water-soluble vitamins
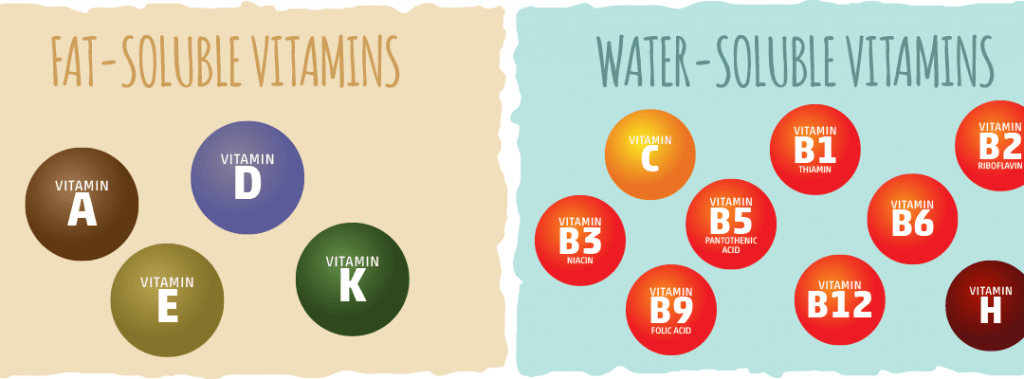
(Source:https://thegoodhealthshop.co.za/2019/03/vitamins-are-divided-into-2-categories/)
Fat-soluble vitamins
- Fat-soluble vitamins are hydrophobic compounds that are stored in our body’s fatty tissue and are only soluble in the presence of dietary fats.
- When a fat-soluble vitamin is ingested, it gets digested by the stomach acid and further digested in the small intestine where bile produced from the liver absorbs the fat-soluble vitamin and nutrient gets absorbed by the wall of the small intestine.
- Then these fat-soluble vitamin travels into the bloodstream or sometimes acts as a carrier for the protein.
Four fat-soluble vitamins are:
- Vitamin A
- Vitamin D
- Vitamin E
- Vitamin K
Vitamins sources and functions
Vitamin A
Vitamin A ( https://thesciencenotes.com/tag/vitamin-a/ ) food sources include leafy vegetables, carrots, sweet potatoes, pumpkin, dairy products like fortified milk, cheese, butter. Vitamin A is essential for vision, to maintain healthy teeth, bone, and skin. Its deficiency causes hardening of the cornea and causes night blindness.
Daily recommended amount of Vitamin A is 900mcg.
Vitamin D sources are egg yolk, liver, fatty fish, mackerel, tuna, salmon, dairy products. Vitamin D is also termed as the sunshine vitamin, when exposed to the sun for about 10-15 minutes three times a week, it produces enough vitamin require for our body. It helps the body to absorb calcium and phosphorous which helps in the development of healthy teeth and bones. When in deficiency causes improper growth of soft bones in kid and also causes rickets.
Daily recommended amount of Vitamin D is 10-20 mcg.
Vitamin E
Vitamin E can be obtained from leafy green vegetables, whole grain products, liver, egg yolk, nuts, and seeds. It acts as an antioxidant which neutralizes the cell-damaging molecules. Vitamin E rich diet may prevent Alzheimer’s disease whereas its deficiency weakens the muscle and damage the red blood cells.
Daily recommended amount of Vitamin E for adult is 15 milligram.
Vitamin K
Vitamin K – rich foods are spinach, broccoli, sprouts, kale, cabbage, asparagus which helps inactivation of proteins for blood coagulation. It also prevents hip fractures. Vitamin K deficiency causes excessive blood loss in case of any injuries and may cause death.
The Daily recommended amount of Vitamin K is 1mcg per kg of the body weight.
Water-soluble vitamins: Vitamins sources and functions
- Vitamin B group and Vitamin C are water-soluble vitamins that dissolve in water and are flushed out of our body through urine. Because they are not stored in our bodies, they should be supplied on a daily basis.
Lists of water soluble vitamins:
- Vitamin B1 (thiamine)
- Vitamin B2 (riboflavin)
- Vitamin B3 (niacin)
- Vitamin B5 (pantothenic acid)
- Vitamin B6 (pyridoxin)
- Vitamin B7 (biotin)
- Vitamin B9 (folic acid)
- Vitamin B12 (cobalamin)
- Vitamin C
Food sources of different vitamins and intake Recommendations:
Vitamin B1
Vitamin B1 is found in all nutritious foods like pork, whole grains, cereals, legumes, and nuts. They help enzymes in metabolism forming energy from carbohydrates. It also helps in the functioning of the heart and nerve cells. B1 vitamin deficiency causes beriberi and dwarfism.
Daily recommended amount of Vitamin B1 for an adult is 1.1mg.
Vitamin B2
Vitamin B2 is present in milk and milk products, leafy vegetables, and whole-grain foods. It is important for normal vision and healthy skin but when deficient causes digestive disorders, skin burning sensation, and cheilosis.
Daily recommended amount of Vitamin B2 is 1.3mg.
Vitamin B3 is rich in meat, poultry, fish, enriched bread and cereals, mushroom, asparagus, peanut butter that has a cholesterol-lowering effect, and maintains healthy skin. Severe deficiency of vitamin B3 causes mental confusion and causes pellagra.
Daily recommended amount of Vitamin B3 is 16mg.
Vitamin B5 foods are beef, poultry, seafood, eggs, milk, vegetables, brown rice, oats which is essential for metabolism and production of hormones and cholesterol. Deficiency is rare but may cause fatigue, insomnia, burning feet, and upper respiratory infections.
Daily recommended amount of Vitamin B5 is 5mg.
Vitamin B6 is also found in meat, poultry, fish, legumes, tofu, potatoes, and non-citrus foods such as bananas that aids in lowering the homocysteine level and also reduce the risk of heart diseases. Deficiency causes conjunctivitis, convulsions, and neurological disorders.
Daily recommended amount of Vitamin B6 is 1.3mg.
Vitamin B7 includes organ meats, egg yolk, soybeans, and fish that provide energy and synthesize glucose. Biotin deficiency causes hair loss, dry mouth, and dry eyes.
Daily recommended amount of Vitamin B7 is 30mcg.
Vitamin B9 contains folic acid foods like fortified grains and cereals, spinach, asparagus, broccoli, black-eyed peas, chickpeas, orange, and tomato juice. It is very essential for pregnant women which helps in preventing brain and spine birth defects in infants. It also reduces colon and breast cancer.
Daily recommended amount of Vitamin B9 is 400mcg.
Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 rich foods are meat, poultry, egg, fish, fortified cereals, and soymilk. It assists in making new blood cells and DNA. Pernicious anemia and a decrease in red blood cells are caused by Vitamin B12 deficiency.
Daily recommended amount of Vitamin B12 is 2.4mcg.
Vitamin C rich foods are citrus fruits and fruit juices, potatoes, bell pepper, strawberries, tomatoes, spinach, cantaloupe, kiwifruit which are rich in antioxidant that helps the body absorb iron and helps in wound healing. Its deficiency causes gum bleeding and scurvy.
Daily recommended amount of Vitamin C is 90mg.
References:
- https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/002399.htm
- https://www.healthlinkbc.ca/health-topics/ta3868
- https://www.helpguide.org/harvard/vitamins-and-minerals.htm
- https://www.health.harvard.edu/staying-healthy/listing_of_vitamins
- https://byjus.com/chemistry/vitamins-types/
- https://oer.unimed.edu.ng/LECTURE%20NOTES/3/2/RASAQ-NURUDEEN-OLAJIDE-UNIMED-BCH-222-VITAMINS.pdf
- https://study.com/academy/lesson/classification-of-vitamins-water-soluble-fat-soluble.html
- https://thesciencenotes.com/tag/vitamin-a/