One of the most essential components of life is blood. Any animal with a circulatory system almost always has blood. According to evolutionary theory, blood is said to have evolved from a specific sort of cell that was in charge of phagocytosis and feeding. Blood and the circulatory system have significantly aided the evolution of more complex lifeforms over the course of billions of years. Blood group testing is described in detail here.
Red, white, and platelet blood cells all compose a human blood cell. All of these blood cells are essential for regulation, protection, and movement. Our red blood cells, or erythrocytes, have antigens and antibodies on their surface that play a major role in determining which blood group we belong to. A blood transfusion from a different blood type might be dangerous.
An important part of medical diagnosis, transfusion medicine, and organ transplantation is determining blood group. Knowing a person’s blood type is important for successful organ transplants, safe and compatible blood transfusions, and lowering the risk of adverse responses. The goal of this page is to give a thorough review of blood group determination, covering its history, procedures, significance, and clinical implications.
History of blood group discovery
The discovery of blood groups has a fascinating history that has had significant effects on medicine. Here are some significant the dates:
Karl Landsteiner (1901):
The ABO blood group system was found in 1901 by Austrian immunologist Karl Landsteiner. He discovered that mixing blood from different people might cause red blood cells to clump together, leading to the classification of blood types into A, B, AB, and O.
Rhesus factor discovery (1940):
Karl Landsteiner and Alexander S. Wiener made the discovery of the Rh factor in 1940. This discovery added another layer of complexity to blood typing, as the Rh factor needed to be considered alongside the ABO system for blood compatibility.
Development of Blood Typing Techniques:
Over the years, various techniques have been developed to determine blood groups accurately. These techniques include the agglutination test, hemagglutination inhibition, and molecular methods like PCR-based assays.
Learn more : https://thesciencenotes.com/components-and-function-of-blood/
Blood group testing procedure
The major goals of this experiment are to identify our blood type and blood group and to understand the basic concepts of the ABO blood group system.
Materials required
- Toothpicks
- Blood sample
- Alcohol Swabs
- Lancet
- Clean glass slide
- Sterile cotton balls
- Biohazard disposal container
- Monoclonal Antibodies (Anti-A, B, and D)
Procedure of Blood Group Test
- Take a clean glass slide and draw three circles on it.
- The Monoclonal Antibodies (MAB) kit should be opened. With the use of a dropper, add Anti-A to the first circle, Anti-B to the second, and Anti-D to the third.
- Keep the slide aside safely without disturbing.
- The alcohol swabs should now be used to gently press the ring finger close to the fingertip, which is where the blood sample will be taken.
- Prick the ring fingertip with the lancet and wipe off the first drop of the blood.
- Allow the blood to drip onto the three glass slide circles as it begins to ooze out by gently pressing the fingertip.
- To stop the flow of blood, apply pressure to the area where it was pierced. If needed, use the cotton ball.
- Mix the blood sample gently with the help of a toothpick and wait for a minute to observe the result.
Conclusion
This chart shows the various blood group types along with their respective Rh factors.
| Blood type | A | B | O | AB |
| Rh-positive | A+ | B+ | O+ | AB+ |
| Rh-negative | A- | B- | O- | AB- |
Precautions in Blood group testing
After using the cotton balls, toothpick, lancet, and alcohol swabs, throw them away. After examining the result, place all the components, including the glass slide, into the biohazard disposal container.
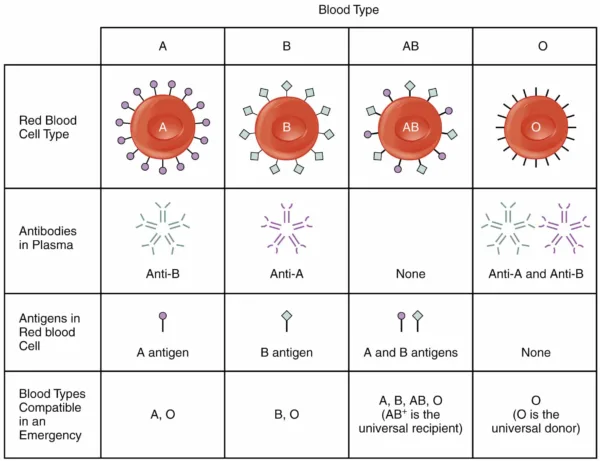
The ABO Blood Group System, which consists of eight different blood types and four major blood groups, was previously stated. Two distinct antigens and antibodies, A and B, are used to classify the individuals into the following groups:
- Group A- Antigen A and Antibody B.
- Group B- Antigen B and Antibody A.
- Group AB- Antigen A and B both and no Antibodies
- Group O- No Antigens and both A and B Antibodies.
The Rh factor is a third type of antigen in addition to these two. The four blood groups are divided into eight distinct blood types depending on whether or not this antigen (Rh factor) exists:
- A positive – Presence of Rh+
- A negative– Presence of Rh-
- B positive- Presence of Rh+
- B negative– Presence of Rh-
- AB positive– Presence of Rh+
- AB negative– Presence of Rh-
- O positive– Presence of Rh+
- O negative– Presence of Rh-
Significance of Blood Group testing
- Blood Transfusions: Ensures safe and compatible blood transfusions, preventing adverse reactions.
- Organ Transplants: Identifies compatible donors for organ transplant recipients, reducing the risk of rejection.
- Pregnancy Management: Helps prevent Rh incompatibility issues during pregnancy that can harm the fetus.
- Emergency Medicine: Critical for immediate blood transfusions in emergency medical situations.
- Medical Diagnosis: Used as a diagnostic tool for certain medical conditions and genetic disorders.
- Forensic Identification: Helps identify individuals in forensic investigations and accidents.
- Research and Clinical Studies: Provides data for medical research, genetic studies, and clinical trials.
- Community Health Planning: Aids in planning for blood supplies during emergencies or outbreaks.
- Preoperative Preparation: Ensures readiness for potential transfusions during surgeries.
- Personalized Medicine: Influences medication choices and dosages in some cases, enhancing personalized treatment approaches.
References
- BYJU’S – Blood Group Test. Retrieved from: https://byjus.com/biology/blood-group-test/
- Testing.com – Blood Typing. Retrieved from: https://www.testing.com/tests/blood-typing/
- Vedantu – Blood Group Test. Retrieved from: https://www.vedantu.com/biology/blood-group-test
- TeleSante – Blood Groups and Residue Factor Setting.
- Healthline – Blood Typing.