Brewing is a beer production process which can be obtained by using basic ingredients like water, malted barley, hops and brewing yeast for the fermentation. The primary starch source is ground cereals or grist and the secondary sources are maize, rice, millet, sorghum and cassava.
The production house of the beer is known as brewery or beer house and the brewing equipments are called plant.
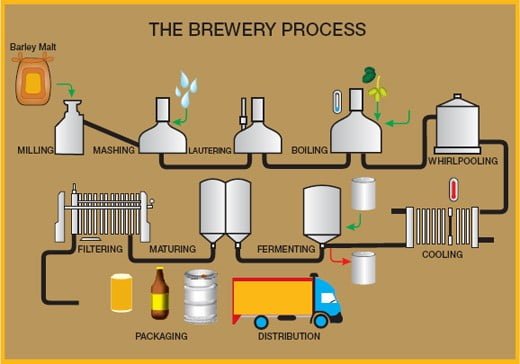
Steps of Brewing
Nine steps are involved during brewing process:
- Malting
- Milling
- Mashing
- Lautering
- Wort boiling
- Wort separation and cooling
- Fermentation
- Filteration and carbonation
- Packaging
(Source: https://www.eightdegrees.ie/brewing-process-2/)
1. Malting
- The most common starch source used is the malted grain which is a key ingredient for the fermentation and provides flavor to the beer.
- The barley grains are cleaned and soaked in water for 24-48 hours and incubated to allow germination for 4 to 5 days.
- During germination, the highly active α-amylase, β-amylase and protease enzymes are formed that converts the starch into a simple sugar to allow further fermentation process. (https://thesciencenotes.com/enzyme-technology/)
- If only barley is used, it develops a dark and unstable color therefore; various malt adjuncts such as dextrose sugar syrup should be used to dilute the product.
- Then, kilning is done at 80°C which is where germinated seeds are heated slowly. Roasting time and temperature differs the flavor and color of the malt.
2. Milling:
- After kilning is completed, the malts are then crushed between the rollers to break the kernels of the malt into cotyledons, making it easy to extract sugar during mashing process.
- Impurities like dust, metals and stones will be separated.
3. Mashing:

- The grains from the milling process are then mixed with a hot water at 65°C for about 1 hour to create a cereal mash.
- When mixed with hot water, starch gets hydrolyzed by it’s naturally occurring enzymes which was already present in malt during germination starts producing simple sugars, maltose, dextrose. Similarly, proteolytic enzyme hydrolyzes proteins into amino acids.
- This conversion process is called saccharification which depends on the pH and temperature.
- Then after saccharification, the sugar rich liquid is obtained which is called wort.
5. Wort boiling:
- Boiling is done for about 60 to 120 minutes depending upon the volume of water and addition of hops in a large tank.
- The boiling process is done for the wort sterilization to remove unwanted microorganisms and also to stop the chemical and enzymatic activity.
- During boiling process, the volatile compounds are removed in vapor and the off-flavor and odor of the wort are also removed out.
- The boiled wort is separated out at the end in a vessel.
6. Wort separation and cooling:
- Solid particles from the hopped wort are separated out in a vessel called whirlpool or settling tank.
- The vessel swirls the wort with a force into a center of the tank and are easily separated.
- The separated worts are brought down to 20-26°C in a plate heat exchanger.
- Water is also added to cool the wort through the gaps of the plate.
7. Fermentation
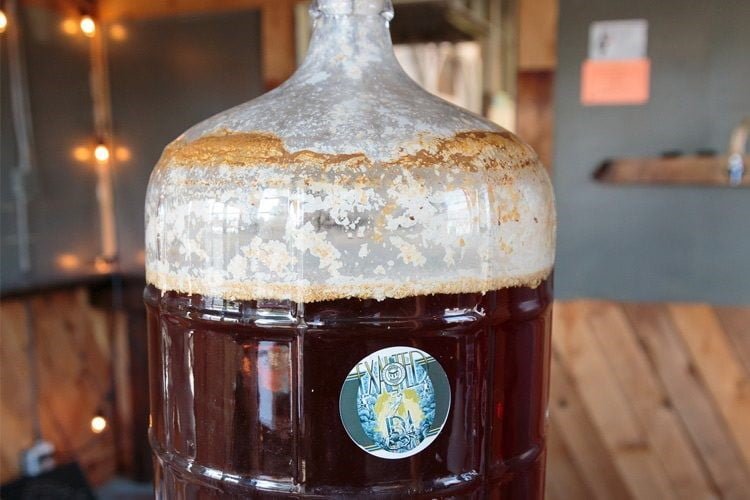

(Source: https://brewfuse.com/how-to-ferment-beer-a-step-by-step-guide/)
- Yeasts are added when the wort is transferred to a fermentation tank.
- Fermentation is carried out in open or closed vessel initially then the secondary fermentation takes place during bottling.
- Saccharomyces cerevisiae is ale yeast that ferments at the top of the wort and Saccharomyces pastorianin is lager yeast that collects at the bottom.
- The temperature is maintained at 60-68°C for ale and 50°C for lager. The temperature for ale is high because it results in ester formation and fragment organic compounds.
- After proper temperature is maintained, the yeast converts the sugar into ethanol and carbondioxide.
- After primary fermentation is completed, the obtained alcohol is conditioned or matured for about a week to year depending on the desired alcohol content.
- The beer is transferred to another container to prevent the formation of unwanted flavours and compounds.
- Krausening is a secondary fermentation done by the addition of wort to active yeast that will restart the fermentation and helps in carbonation and eliminates unwanted compounds.
8. Filtration and carbonation:
- Sheet pad filters are used to filter the beer that allows particles smaller than the pore size to pass.
- These filter sheets are disposable and are replaced between each batch.
- Beers are then carbonated by adding CO2 under high pressure. Carbonation can also be done by addition of sugar, yeast and hops.
- Carbonation allows clarification in the beer.
10. Packaging/bottling:

(Source:https://www.fotosearch.com/CSP588/k65627537/)
- After carbonation, beer is transferred to a bright beer tank which takes about 3 to 4 weeks to complete the cellering process.
- Finally the beer gets ready to be packed which is usually done in bottles, cans and barrels.
References:
- https://firstwefeast.com/drink/learn-how-to-brew-beer-with-these-fun-animated-gifs
- https://www.onlinebiologynotes.com/brewing-beer-production-process/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780123738912000018
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Brewing
- https://beerconnoisseur.com/articles/beer-101-fundamental-steps-brewing?page=3